Assessment
What can be assessed?- Readiness. Do students already know some concepts? What prior knowledge do they have? What skills do they have? This is why pre-assessment is important.
- Students' Interest. What students like outside of class. Knowing their interests will help us engage them.
- Learning Profile. Areas of strength and weakness, work preferences, and self-awareness.
What is an assessment? Measuring students' knowledge and keeping track of it.
3 Types of Assessment
- Diagnostic: Finding out. Belongs in the introduction of the unit. (KWL chart, pre-assessment).
- Formative Assessment: Keeping track and checking up. Occurs throughout the lesson. (exit ticket, conference, quiz, journal entry, check for understanding)
- Summative Assessment: Making sure, at the end of the lesson, independent practice. (unit test, post-assessment, performance task)

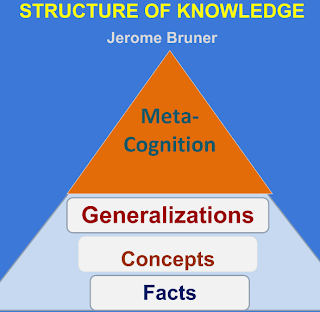
Building Blocks & Components of Objectives
Condition: the setting. (given task or materials. only one setting)
Behavior: action expressed by a verb. (only one verb)
Criterion: expected performance level (no percentages. only one)
*Objective is written in the independent practice part of the lesson plan (the end). When students work alone they show that they really learned something.
*Objective is written in the independent practice part of the lesson plan (the end). When students work alone they show that they really learned something.
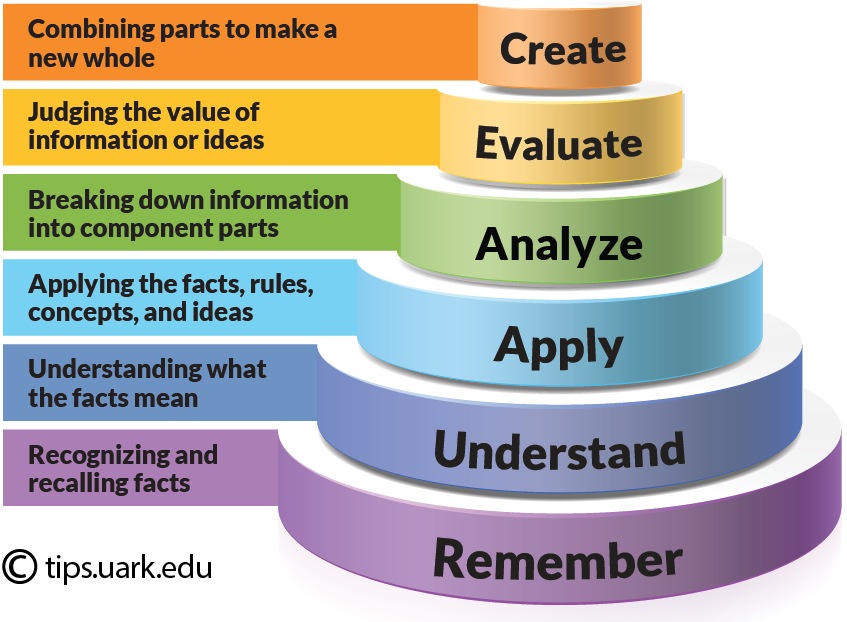
Objective Formula: Given (a task or materials) the student will (a verb from Bloom's Taxonomy) with (an expected level of performance).
*the materials in the objective are not the teacher's materials, they are the student's materials.
*the objective is singular; one student.
*you must create a rubric for the objective.
Objective example: Given a task to work in a group of 4 and the resources on the American Revolution, the student will create a poster, following the criteria of the rubric and scoring at 3/4.